Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for
Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders
Things you need to know about Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)
What is deep brain stimulation (DBS)? When is it used? How does it work?
How is DBS surgery performed? What are its risks, complications & benefits?
What is the recovery, success rates and hospital costs of DBS surgery?
What is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)?
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical procedure for the treatment of many types of neurological problems. It is specifically useful for the management of disabling neurological symptoms of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and other movement disorders.
What is Deep brain stimulation (DBS)?
When is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) indicated?
DBS is indicated in the management of essential tremor and dystonia in patients with parkinson’s disease and other movement disorders. The procedure is suitable for people who have had:
- Parkinson’s disease for at least four years
- Respond to parkinson’s disease medication but have developed motor complications over time
- Have intact cognitive functions
- No serious underlying systemic illness
- Have no signs of severe vascular disease, extensive atrophy, or signs of atypical parkinson’s disease in the MRI of the brain.
How does Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) work?
During the DBS surgery, leads are implanted on targeted brain areas and a battery-operated medical device called a neurostimulator is implanted in the chest. The DBS system delivers electrical stimulation to targeted areas in the brain that control movement, thereby blocking the abnormal nerve signals responsible for causing tremor and other symptoms of parkinson’s disease.
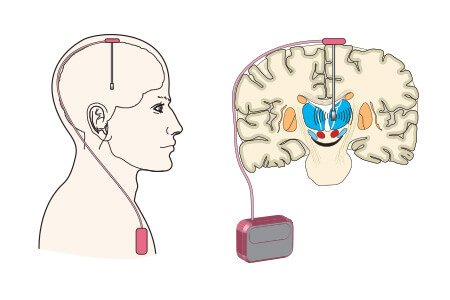
How is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgery performed?
Identifying the brain target: Before the procedure is done, the exact target brain areas where electrical nerve signals generate PD symptoms, are identified with the help of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) or Computed Tomography (CT) scanning or microelectrode scanning.
How is DBS surgery performed?
Surgery: The surgery involves two stages:
- First stage: Thin wires or electrodes are placed into the specific target area of the brain. The patient is kept awake to perform certain tasks to ensure that the electrodes are positioned correctly.
- Second stage: On the same day or next day,the electrodes are connected to a battery-operated device called impulse generator battery (IPG) or neurostimulator, by an insulated wire passing under the skin of the head, neck and shoulder. The neurostimulator is then implanted under the skin below the collarbone.
Programming: The IPG is turned on and adjusted 2-4 weeks after surgery and may take a few weeks before patients receive adequate symptom relief. The patient receives initial programming of the neurostimulator so that it delivers continuous electrical pulses through the electrodes. These impulses interfere with and block the electrical signals that cause PD symptoms. All parts of the stimulator system are located internally. Patients may also receive a hand held device to check battery and switch on and off the device.
What are the risks and complications of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) vs its benefits?
Some benefits of DBS include:
- Significant improvement in all the symptoms related to PD
- Significant reduction of medication
- Unlike many other surgeries of brain, DBS does not cause any irreversible damage to brain tissues and is therefore considered a safer option
- The electrical stimulation can be adjusted depending on the patient’s response to the medication and changes in the course of disease
- The stimulator can be turned off at any given time if required
Some complications due to surgery include:
- Bleeding in the brain
- Breathing problems
- Confusion, change in mood, memory and thinking
- Device complications, such as loose wire, an eroded lead wire or lead in the wrong place
- Headache, dizziness, and tingling
- Heart problems
- Infection
- Mood changes, like mania and depression
- Nausea
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Problem in speech, balance and lightheadedness
- Problems in movement and speech that get worsen
- Seizures
Some side effects of stimulation include:
- Stroke symptoms, like numbness and slurred speech
- Temporary pain and swelling at the site of implantation
- Tightness of muscles in the face or arm
What is the success rate of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)?
- Studies report that DBS can reduce off -periods PD symptoms by 60% (fluctuations in motor symptoms due to poor response to medicines).
- By reducing the need of medication, DBS rapidly decreases medication-induced dyskinesias by 60 to 80% and improves quality of life in people with advanced PD.
- DBS motor benefits have been reported to remain clinically evident for as long as 10 years.
Recovery after Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS):
Considering the surgery was free of any complications, the patient is kept under monitoring and discharged after 3 to 5 days of the procedure. However, patient is required to follow his scheduled outpatient visits for initial programming and support. Once discharged from the hospital, the patient can gradually resume his/her normal life.

Recovery after DBS
What factors should be considered while choosing a hospital for Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) surgery?
DBS is a major surgery and for the best possible outcomes, it is extremely important to choose a center with an expert team of neurosurgeon, neurologist, and health care team trained and experienced in DBS therapy. In addition to an expert surgical team, the hospital should have proper support infrastructure like intraoperative diagnostics, neurosurgery room (OT) and neuro intensive care unit (NICU) to fulfill the pre-operative and post-operative needs.
What factors govern the cost of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS)?
The cost of surgery usually depends on various factors like:
- Experience and expertise of the DBS neurosurgeon and team
- Underlying comorbidities and age of the patient which may affect the hospital stay and requirement of additional tests and medication
- DBS system – electrode, pulse generator and hand held device
- Room category availed as per the hospital billing policy
To know more about DBS surgery, you can request for a call back and our DBS surgery specialist will call you and answer all your queries.
Related blogs you may like to read:
References:
- Deep brain stimulation. Available at https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/deep-brain-stimulation/about/pac-20384562. Accessed on March 27, 2018.
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease Patients. Available at https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/4080-deep-brain-stimulation-for-parkinsons-disease-patients. Accessed on March 27, 2018.
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Available at https://www.ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/All-Disorders/Deep-Brain-Stimulation-Parkinsons-Disease-Information-Page. Accessed on March 27, 2018.
- Deep Brain Stimulation for Parkinson’s Disease. Available at https://www.webmd.com/parkinsons-disease/guide/dbs-parkinsons#3. Accessed on March 27, 2018.
- De Souza RM, Moro E, Lang AE, et al. Timing of Deep Brain Stimulation in Parkinson Disease: A Need for Reappraisal? Ann Neurol. 2013 May; 73(5): 565–575.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) – Frequently Asked Q & A’s. Available at http://www.tremor.org.uk/deep-brain-stimulation-faq.html. Accessed on March 27, 2018.









