Stereotactic Radiosurgery – SRS
Stereotactic radiosurgery or SRS is a non-invasive radiation therapy used to treat small tumors (up to 3 cm in diameter) and brain functional abnormalities. SRS delivers precisely targeted radiation in the form of multiple beams angled to collide on the exact spot of the brain.
SRS is used to treat any abnormalities in the brain and spine – such as tumors and cancers, epilepsy, trigeminal neuralgia, and arteriovenous malformations. Some significant stereotactic radiosurgery procedures include treating lesions in the spine, craniopharyngiomas, glioblastomas, gliomas, hemangioblastomas, meningiomas, pineal tumors, pituitary tumors, and so on. Stereotactic radiosurgery for trigeminal neuralgia (or tic douloureux) is one of the most common applications.
Oncologists may advise multiple sessions of stereotactic radiosurgery for larger tumors (> 1 inch in diameter). This type of stereotactic radiosurgery is called fractionated radiosurgery, in which radiation is delivered in up to five sessions.
1. What is stereotactic radiosurgery?
The stereotactic radiosurgery delivers high-dose radiation in a single sitting or 2 to 5 sittings for treatment. The stereotactic radiosurgery helps to shrink or contain the growth of the tumor while preserving surrounding healthy tissue.
2. Which patients are good candidates for SRS?
SRS is reserved for tumors less than 3 centimetres in diameter. It is commonly applied to patients with metastatic brain tumors of smaller sizes like vestibular schwannoma or acoustic neuroma and for abnormalities like arteriovenous malformations, arteriovenous fistulas, and tremors.
Used for treating tumors that are:
- Located close to vital organs and anatomic regions.
- Hard to reach.
- May move within the body.
- Primary and metastatic tumors.
- Residual tumor cells following surgery.
3. How is SRS given?
SRS is teamwork involving radiation oncologists, neurosurgeons, dosimetry experts, and physicists. It is performed on an outpatient basis over 15 to 60 minutes. It is suggested to consult your doctor regarding driving post-treatment and if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, taking an oral medication or insulin.
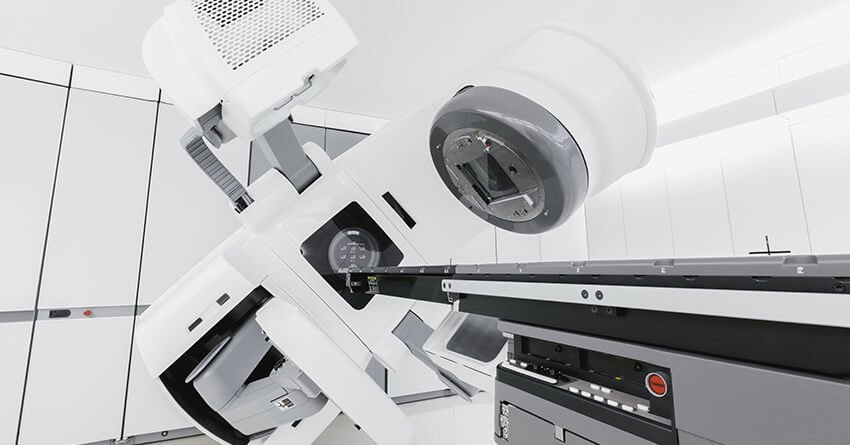
You would spend several hours in the daycare center for preparation, the procedure, and post-treatment observation. The head frame during stereotactic radiosurgery would help keep your head perfectly still, while a computer-controlled mechanized arm moves around shooting radiation beams from different angles.
3D imaging techniques (like CT, MRI, and PET/CT) help detect, measure and focus multiple radiation beams on the target even if the body moves.
4. What are the benefits of SRS?
SRS has many benefits for patients:
- Live 3D mapping for complete accuracy.
- Treatment of small tumors close to critical organs.
- Treatment of hard-to-reach tumors and regional abnormalities.
- Minimal damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
- Better outcomes.
- Shorter overall treatment time.
5. What is SRS cancer treatment?
SRS is similar to any radiation treatment where instead of removing the tumor, it damages the DNA of tumor cells, inhibiting its growth and reproduction. It helps to shrink benign tumors (between 18 to 24 months) and malignant and metastatic tumors (under 4 months).
The SRS aims to prevent tumor growth; therefore, its stoppage and shrinkage are successful outcomes.
6. Is a gamma knife the same as stereotactic radiosurgery?
Gamma knife radiosurgery is a non-invasive procedure that fires close to 200 radiation beams to treat minor to medium-sized intracranial lesions. Gamma knife radiosurgery passes through four phases – placement of the head frame, imaging of the target location, computerized dose planning and radiation delivery.
7. How long does stereotactic radiosurgery take?
Stereotactic radiosurgery of the brain and spine is typically completed in a single session. It takes about 15-60 minutes for the actual procedure, but you must stay in the daycare center for a few hours with a family member or a caregiver.
8. Is CyberKnife the same as stereotactic radiosurgery?
CyberKnife and TrueBeam are the brand names of the manufacturer of linear accelerator (LINAC), used to treat tumors and other abnormalities in the brain.
9. Is stereotactic radiosurgery a surgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery uses precisely focused radiation beams to treat tumors without any incision or opening on the skin and no general anaesthesia is administered to adults. In the traditional sense of the word, it is not a surgical procedure. SRS uses 3D imaging to target high doses of radiation to the affected area with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
10. Why should I choose Yashoda Hospitals for stereotactic radiosurgery?
Yashoda Hospitals has experts with the latest and most advanced equipment to offer the best SRS treatment. The team at Yashoda Cancer Institute (the radio-oncology department) deserves special mention as experts are well-trained and well experienced. In addition, state-of-the-art daycare centers, diagnostics and imaging, ICUs and other world-class facilities are available.
Patient Testimonials For Cancer