Thyroid Cancer: Insights into the Butterfly Gland’s Battle
Understanding Thyroid Cancer
Though the butterfly-shaped thyroid gland in your neck plays a vital role in regulating hormones and metabolism,it can also be the focus of concern, particularly when it comes to thyroid cancer. Thyroid cancer is more common than many people realize. It is the seventh most common cancer in women, usually affecting people between the ages of 25 and 65, and it is on the rise everywhere, underscoring the need for more awareness and vigilance.
Risk Factors for Thyroid Cancer
Knowing the risk factors can help individuals and healthcare providers assess the likelihood of developing thyroid cancer:
- Age:The risk increases within the 25 to 65 age bracket.
- Gender: Women are more susceptible than men.
- Radiation Exposure: A history of radiation exposure to the head and neck area raises the risk.
- Goiter: A prior diagnosis of goiter, an enlarged thyroid, is a potential risk factor.
- Family History: A family history of thyroid cancer can heighten the risk.
- Genetic Conditions: Specific genetic conditions, such as Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) syndromes, can predispose individuals to thyroid cancer.
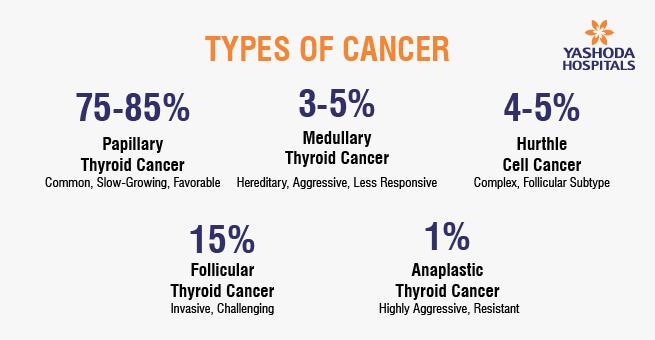
Types of thyroid cancers:
Papillary Thyroid Cancer (PTC): Papillary thyroid cancer, the most common type, is slow-growing and typically remains confined to the thyroid gland. Treatment includes surgical removal of the affected thyroid lobe or the entire gland, followed by radioactive iodine therapy for excellent survival rates.
Follicular Thyroid Cancer: Follicular thyroid cancer, less common but manageable when caught early, may spread to nearby lymph nodes. Treatment involves surgical removal of the affected thyroid lobe or the entire gland, with the option of radioactive iodine therapy for a generally favorable prognosis.
Hurthle Cell Cancer (HCC): Hurthle cell cancer, a rare and aggressive subtype of follicular thyroid cancer, often requires total thyroidectomy, followed by radioactive iodine therapy and, in some cases, external radiation therapy. Long-term monitoring is essential.
Medullary Thyroid Cancer (MTC): Medullary thyroid cancer, accounting for a small percentage of cases, is more aggressive and may spread to lymph nodes. The primary treatment is total thyroidectomy, with genetic testing recommended. Some cases respond to targeted therapies like tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer (ATC): Anaplastic thyroid cancer, extremely rare and highly aggressive, requires a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and, occasionally, chemotherapy.
Are you ready to empower yourself with knowledge and take control of your thyroid health?
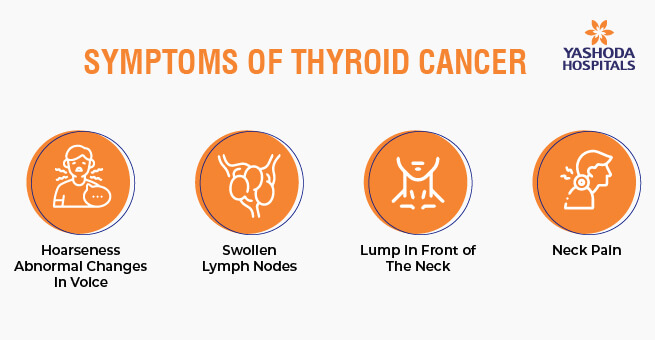
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms
Common indicators include a palpable lump in the neck, hoarseness, swollen neck glands, difficulty swallowing or breathing, throat or neck pain, and a persistent unexplained cough. Being vigilant about these symptoms can lead to early detection.
Diagnosis:
- Check-ups: Healthcare providers conduct a thorough neck examination.
- Blood Tests: A thyroid profile is essential to assess hormone levels.
- Ultrasound: Neck ultrasound offers detailed imaging of the thyroid.
- Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAC) and lymph node biopsy are critical for confirming cancer.
- Imaging: CT scans provide a broader view of the neck and chest, while PET CT is used in specific cases.
Treatment Options
- Surgery: Surgical procedures range from partial thyroid removal (hemithyroidectomy) to complete removal (total thyroidectomy).
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: This targeted treatment destroys any remaining thyroid tissue post-surgery.
- External Beam Radiation Therapy: Used after surgery for medullary and anaplastic thyroid cancers.
- Chemotherapy: Rarely employed, primarily in inoperable or advanced cases.
- Targeted Therapy: This includes drugs like tyrosine kinase inhibitors and protein kinase inhibitors, aiming at specific cancer-related molecules.

Thyroid Cancer: Awareness and Empowerment
Thyroid cancer is a complex condition, but understanding its nuances, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health. With early detection, appropriate treatment, and diligent follow-up care, many individuals with thyroid cancer can achieve favorable outcomes and continue to lead healthy lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are thyroid cancers treatable?: Yes, thyroid cancer is highly treatable, especially when detected early. Survival rates are excellent for early-stage cases.
Does thyroid cancer come back?: Yes, thyroid cancers can relapse, even after many years. Regular follow-up care helps detect and manage potential recurrences.
Can thyroid cancer spread?: Untreated or late-stage thyroid cancer can spread to nearby lymph nodes and organs, and in advanced cases, even to the lungs or bones.
References:
- Thyroid Cancer https://www.cancer.gov/types/thyroid/patient/thyroid-treatment-pdq
- Thyroid Cancer: Symptoms and Causes https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/thyroid-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20354161
- Thyroid Cancer: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Treatment https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/12210-thyroid-cancer
- Thyroid Cancer https://medlineplus.gov/thyroidcancer.html
About Author –